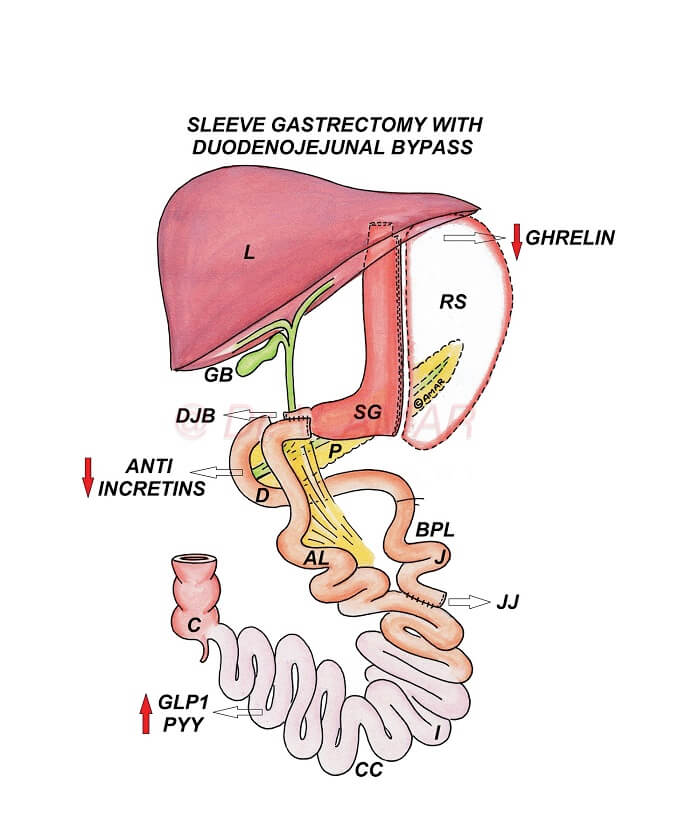
LAPAROSCOPIC SG DJB
ROBOTIC, LAPAROSCOPIC SLEEVE GASTRECTOMY WITH DUODENOJEJUNAL BYPASS (SG DJB)
– It is a type of sleeve plus bypass combination surgery (Sleeve plus procedure) for the treatment of severe obesity and severe diabetes.
– It is a modification of biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch (BPD DS), with a more proximal anastomosis (duodenojejunal anastomosis in place of duodenoileal anastomosis).
– Procedure:
- Performed by robotic or laparoscopic method (By putting small holes over the tummy) using advanced high quality imported laparoscopic equipment and instruments.
- Up to 80% of the stomach is removed using high quality staplers and stapler guns to form a vertical sleeve.
- When the stomach is divided using staplers, it is stapled in three rows, sealed and cut simultaneously.
- The percentage of the removed stomach is relative but the capacity of the remaining gastric sleeve is 60 to 100 ml.
- First part of the duodenum (First part of the small intestine) is divided using high quality staplers and stapler guns.
- Divided first part of the duodenum is attached to the mid jejunum (Middle part of the small intestine) in a Roux en y fashion (Duodenojejunal bypass).
– In India and Asia,
- Individuals suffering from severe obesity with the body mass index is ≥ 32.5 kg/m2 with co-morbid medical conditions such as type 2 diabetes.
- Individuals suffering from severe obesity with the body mass index is ≥ 37.5 kg/m2 even without any co-morbid medical conditions.
– In Western countries
- Individuals suffering from severe obesity with the body mass index is ≥ 35 kg/m2 with co-morbid medical conditions such as type 2 diabetes.
- Individuals suffering from severe obesity with the body mass index is ≥ 40 kg/m2 even without any co-morbid medical conditions.
– Weight loss is mainly due to physiological changes altering body energy balance.
– Because of these changes
- Appetite (Hunger) is reduced.
- Metabolic rate is increased.
- Energy expenditure is increased.
- ‘Fat mass’ is reset to a lower level.
- Fat starts melting as body doesn’t want to store large quantity of fat.
- You don’t eat large quantity of food as you start hating unhealthy foods.
– Physiological changes are significantly high as undigested food directly enters from 1st part of the duodenum into mid jejunum and rapidly reaches distal ileum.
– Diversion of the biliopancreatic juices contribute further to these physiological changes.
– Role of food restriction and malabsorption is secondary.
– Same physiological changes are responsible for type 2 diabetes remission.
- Insulin resistance is reduced.
- Insulin production is optimised to control blood sugars.
– Average excess weight loss is ~ 60 to 70%.
– Some may lose above average, even 100% of the excess weight loss but that number is less.
– For Example – If you are 50 kg excess weight, you lose approximately 30 to 35 kg on average. Some may lose all the extra 50 kg but that number is less.
– Generally if your weight burden is less, you lose more percentage of excess weight and if your weight burden is more you lose less percentage of excess weight.
– Total weight loss percentage is ~ 25 to 30%.
– Average diabetes remission ~ 60 to 70%.
– It is necessary to follow lifestyle modifications to improve weight loss and diabetes remission and to prevent weight regain and diabetes recurrence.
– Results in long lasting weight loss.
– Results in long lasting diabetes remission.
– Physiological changes are relatively high in Sleeve with duodenojejunal bypass as longer small intestine is bypassed compared to the standard Gastric sleeve (SG).
– Weight loss is more effective & long lasting after SG DJB compared to the standard SG.
– Diabetes remission is relatively high & durable after Sleeve with duodenojejunal bypass compared to the standard SG.
– Weight loss and diabetes remission after SG DJB are comparable to that of Roux En Y Gastric Bypass.
– Weight regain after SG DJB is low.
– Diabetes recurrence after SG DJB is low.
– SG DJB has several advantages compared to RYGB and MGB – OAGB.
- There is no ‘at risk’ stomach remnant.
- Calcium and iron deficiency risk is low since first part of the duodenum is not bypassed
- Risk of dumping syndrome is less because of intact pylorus controlling food out put
- There is no risk of marginal ulcers
– Compared to BPD DS, risk of protein energy malnutrition, malabsorption and vitamin & mineral deficiencies is very low because common channel (intestine available for digestion and absorption) is very long.
– SG DJB is technically more advanced, complex and time taking compared to SG, RYGB and MGB – OAGB.
– It needs advanced laparoscopic surgical skills and training.
– There is loss of endoscopic access to biliary tract (Pathway connecting liver and small intestine).
– SG DJB is less effective compared to Mini Gastric Bypass (One Anastomosis Gastric Bypass), Sleeve plus bypass combination surgeries such as Sleeve gastrectomy with loop duodenojejunal bypass (SG LDJB), Sleeve gastrectomy with duodenoileal interposition (SG DII), Sleeve gastrectomy with loop gastroileal bypass (SG LGIB), Single anastomosis duodenoileal bypass with sleeve (SADI S) and BPD DS because bypassed small intestine (biliopancreatic limb) is relatively shorter.
– Some may lose below average. Inadequate weight loss ~ 15%. They may lose only 5 to 10 kg and stop losing further.
– Average weight regain ~ 25 to 35%.
– Diabetes recurrence after SG DJB is ~ 35 to 45%.
– If anyone regains weight or if diabetes recurs after Sleeve with duodenojejunal bypass, revision to Loop duodenal switch or Duodenal switch re-induce significant weight loss and diabetes remission.
– It is very very safe procedure.
– It is a life saving surgery.
– Severe obesity and severe diabetes are dangerous.
– Bariatric and Metabolic surgeries are very safe.
– Complications are very rare. Even if they occur, they can be rectified.