Laparoscopic Adjustable Gastric Banding (LAGB)
ROBOTIC, LAPAROSCOPIC ADJUSTABLE GASTRIC BANDING (LAGB)
– Once popular for the treatment of severe obesity and severe diabetes, it became outdated and numbers declined worldwide because of less efficacy and availability of better surgeries.
– Procedure:
- Performed by robotic or laparoscopic method (By putting small holes over the tummy) using advanced high quality imported laparoscopic equipment and instruments.
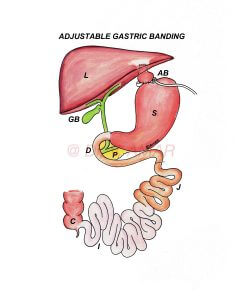
- An inflatable silicon band is wrapped around the upper part of the stomach.
- Capacity of stomach above this band will be < 20 ml.
- Individuals can’t take large quantity of food at a time.
- This band has a balloon which is connected through a tube to an access port fixed outside abdominal muscles.
- By injecting or withdrawing saline from the access port, opening between the pouch and remaining stomach can be adjusted there by controlling the food intake.
– In India and Asia,
- Individuals suffering from severe obesity with the body mass index is ≥ 32.5 kg/m2 with co-morbid medical conditions such as type 2 diabetes.
- Individuals suffering from severe obesity with the body mass index is ≥ 37.5 kg/m2 even without any co-morbid medical conditions.
– In Western countries
- Individuals suffering from severe obesity with the body mass index is ≥ 35 kg/m2 with co-morbid medical conditions such as type 2 diabetes.
- Individuals suffering from severe obesity with the body mass index is ≥ 40 kg/m2 even without any co-morbid medical conditions.
– Gastric banding is purely a restrictive procedure.
– It acts mainly by limiting calorie intake.
– Physiological changes responsible for weight loss after gastric banding are negligible unlike other bariatric and metabolic surgeries.
– Average excess weight loss is < 50%.
– Some may lose above average, even 100% of the excess weight loss but that number is less.
– For Example – If you are 50 kg excess weight, you lose approximately < 25 kg on average. Some may lose all the extra 50 kg but that number is less.
– Generally if your weight burden is less, you lose more percentage of excess weight and if your weight burden is more you lose less percentage of excess weight.
– Total weight loss percentage is ~ 15 to 20%.
– Average diabetes remission < 50%.
– It is necessary to follow lifestyle modifications to improve weight loss and diabetes remission and to prevent weight regain and diabetes recurrence.
– It is easy to perform.
– Complications are few
– Hospital stay is short (less than 1 day).
– Since there are negligible physiological changes after LAGB, weight loss and diabetes remission are inadequate.
– Weight regain chances are very high.
– Majority of patients want to get band removed because of intolerance and increased hunger.
– There is a need for regular visits to the doctor for repeated adjustments of the band.
– After this operation food intolerance, band slippage, band erosion, pouch dilatation or gastric prolapse can occur.
– It is very very safe procedure.
– It is a life saving surgery.
– Severe obesity and severe diabetes are dangerous.
– Bariatric and Metabolic surgeries are very safe.
– Complications are very rare. Even if they occur, they can be rectified.