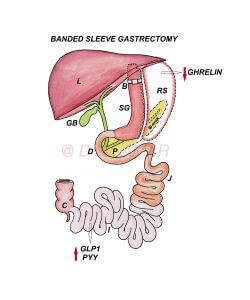
Laparoscopic BANDED SG
LAPAROSCOPIC BANDED SLEEVE GASTRECTOMY
or
LAPAROSCOPIC BANDED GASTRIC SLEEVE SURGERY
(Laparoscopic BANDED SG)
– Most commonly performed bariatric surgery worldwide for the treatment of severe obesity and severe diabetes.
– Procedure:
- Performed by robotic or laparoscopic method (By putting small holes over the tummy) using advanced high quality imported laparoscopic equipment and instruments.
- Up to 80% of the stomach is removed using high quality staplers and stapler guns to form a vertical sleeve.
- When the stomach is divided using staplers, it is stapled in three rows, sealed and cut simultaneously.
- The percentage of the removed stomach is relative but the capacity of the remaining gastric sleeve is 60 to 100 ml.
- A loose ring is placed around upper part of sleeve, with the intention of creating long term restriction.
– In India and Asia,
- Individuals suffering from severe obesity with the body mass index is ≥ 32.5 kg/m2 with co-morbid medical conditions such as type 2 diabetes.
- Individuals suffering from severe obesity with the body mass index is ≥ 37.5 kg/m2 even without any co-morbid medical conditions.
– In Western countries
- Individuals suffering from severe obesity with the body mass index is ≥ 35 kg/m2 with co-morbid medical conditions such as type 2 diabetes.
- Individuals suffering from severe obesity with the body mass index is ≥ 40 kg/m2 even without any co-morbid medical conditions.
– Sleeve gastrectomy is ideal for individuals with excess weight burden of 20 to 30 kg with or without mild diabetes or co-morbid conditions.
– Sleeve gastrectomy is considered in teenagers and in females planning for pregnancy in future.
– Weight loss is mainly due to physiological changes altering body energy balance.
– Because of these changes
- Appetite (Hunger) is reduced.
- Metabolic rate is increased.
- Energy expenditure is increased.
- ‘Fat mass’ is reset to a lower level.
- Fat starts melting as body doesn’t want to store large quantity of fat.
- You don’t eat large quantity of food as you start hating unhealthy foods.
– Role of food restriction and malabsorption is secondary.
– Same physiological changes are responsible for type 2 diabetes remission.
- Insulin resistance is reduced.
- Insulin production is optimised to control blood sugars.
– Creating too tight sleeve with the expectation that it will provide more weight loss and more diabetes remission is wrong.
– Too tight sleeve will increase the risk of complications such as leak and vomitings, but will not provide additional weight loss.
– I prefer creating lax sleeve so that weight loss and diabetes remission will be sufficient, at the same time complications are very rare.
– Since weight loss and diabetes remission are mainly related to physiological changes and role of restriction or malabsorption is secondary, placing a ring around gastric sleeve doesn’t offer any extra advantage in terms of weight loss, diabetes remission, prevention of weight regain or diabetes recurrence.
– Average excess weight loss is ~ 50 to 60%.
– Some may lose above average, even 100% of the excess weight loss but that number is less.
– For Example – If you are 50 kg excess weight, you lose approximately 25 to 30 kg on average. Some may lose all the extra 50 kg but that number is less.
– Generally if your weight burden is less, you lose more percentage of excess weight and if your weight burden is more you lose less percentage of excess weight.
– Total weight loss percentage is ~ 20 to 25%.
– Average diabetes remission ~ 50 to 60%.
– It is necessary to follow lifestyle modifications to improve weight loss and diabetes remission and to prevent weight regain and diabetes recurrence.
– Very simple and safe surgery.
– Results in long lasting weight loss.
– Results in long lasting diabetes remission.
– Complications are very low.
– Compared to diversion procedures risk of vitamin and mineral deficiencies is very low.
– Dumping syndrome is rare.
– Physiological changes are less in sleeve gastrectomy compared to the diversion surgeries.
– Weight loss is less effective after gastric sleeve compared to the diversion procedures.
– Diabetes remission is less after sleeve gastrectomy compared to the diversion procedures.
– Weight regain after gastric sleeve is very high.
– Some may lose below average. Inadequate weight loss ~ 20%. They may lose only 5 to 10 kg and stop losing further.
– Average weight regain ~ 30 to 40% especially if lifestyle modifications are not followed.
– Diabetes recurrence after sleeve gastrectomy is very high ~ 40 to 50%.
– Placing a band may at most postpone weight regain or diabetes remission but can’t prevent them.
– Incidence of reflux of acid into esophagus is high after gastric sleeve.
– If anyone regains weight or if diabetes recurs after sleeve gastrectomy, revision to loop duodenal switch or duodenal switch re-induce significant weight loss and diabetes remission.
– It is very very safe procedure.
– It is a life saving surgery.
– Severe obesity and severe diabetes are dangerous.
– Bariatric and Metabolic surgeries are very safe.
– Complications are very rare. Even if they occur, they can be rectified.
– Band related complications such as band slippage, and band erosion are rare.